Aging is an unavoidable biological process, while aesthetic medicine offers breakthrough methods for individuals to maintain a youthful appearance. The latest developments in anti-aging aesthetics are being produced with the fast evolution of injectable neurotoxins, bio-remodeling procedures, and more. In this article, we will discuss recent advancements in anti-aging treatments and will cover their effectiveness, safety, and mechanisms of action.
Botox and Neuromodulators
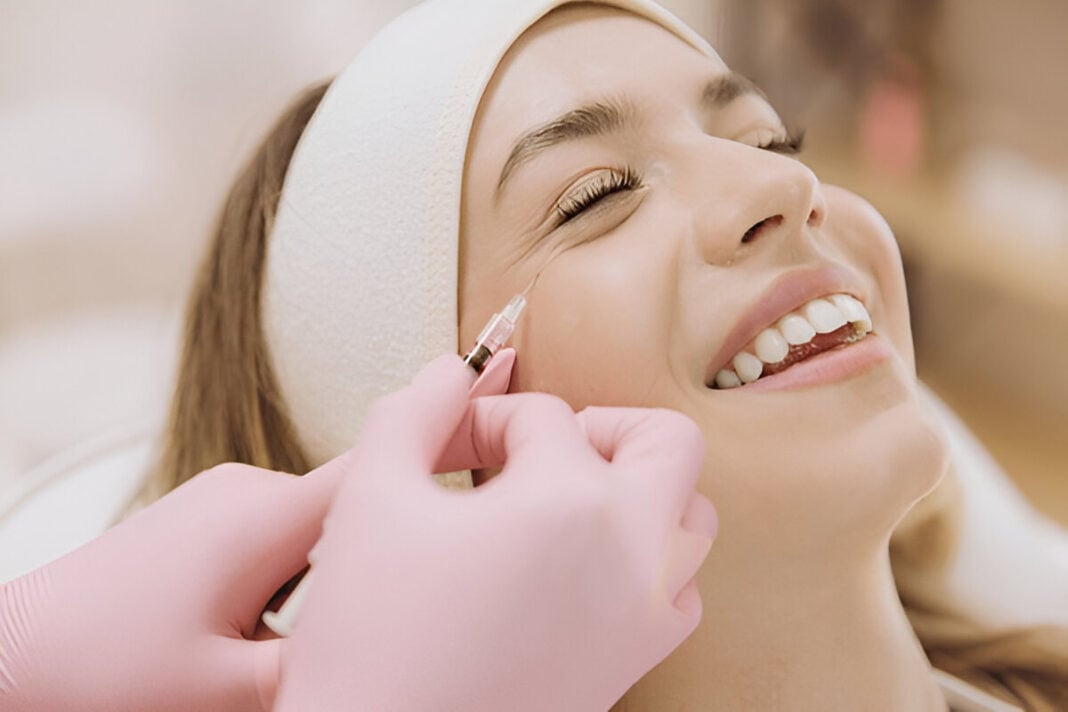
Botulinum toxin is undoubtedly one of the popular anti-aging treatments for facial wrinkles that has been in use for decades. Botox and its counterparts Dysport and Xeomin temporarily paralyze underlying muscles, thus stopping dynamic wrinkles from occurring (Carruthers & Carruthers, 2021). Treatments are specifically useful for forehead lines, crow’s feet, and frowns. Recently manufactured products have longer-lasting formulations, more precise targeting of specific facial muscles, and preservation of natural expression (Alster & Lupton, 2020).
Dermal Fillers: Hyaluronic Acid and Beyond
Hyaluronic acid (HA)-based dermal fillers are probably one of the most important options in non-surgical facial rejuvenation. These fillers restore lost volume to the face and smooth wrinkles and enhance contours (De Maio, 2018). Novel fillers have been developed for extended duration, enhanced cross-linking technologies, and fillers for localized facial areas such as the tear troughs and jaws. Collagen-stimulating fillers such as Sculptra (poly-L-lactic acid) and Radiesse (calcium hydroxylapatite) have also gained acceptance, as they are perceived to promote the formation of natural collagen (Goldie et al., 2022).
Bio-Remodeling: A New Frontier
Dermal bio-remodeling takes a modern approach in aesthetics that instead of only considering wrinkles, gives precedence to skin quality and hydration. Profhilo is one of the latest and most innovative bio-remodeling treatments, which is a pure injectable HA that flows through the skin to promote hydration, elasticity, and firmness (Di Pietro et al., 2021). Rather than volumizing, Profhilo improves the skin texture, promoting the synthesis of collagen and elastin.
Regenerative Aesthetics: PRP and Stem Cell Therapy
Aesthetics became an outlet for regenerative medicine via treatments such as platelet-rich plasma and stem cell therapy. PRP therapy consists of extracting the patient’s blood and centrifuging it to concentrate growth factors, which then are reinjected into the skin to stimulate collagen production and tissue repair (Sclafani, 2017). On the other hand, stem cell-based treatments are being evaluated for their capability to rejuvenate aging skin at the cellular level; however, more studies would need to be done to verify long-term efficacy (Rigotti et al., 2016).
Energy-Based Devices: Laser and Radiofrequency Treatments
Alternative non-invasive options for skin tightening and resurfacing have seen phenomenal advancement with the development of laser and radiofrequency (RF) treatments. Fractional laser technologies such as CO2 and Erbium lasers are effective against fine lines, sun damage, and acne scars (Tierney et al., 2018). RF-based treatments, such as Thermage and Morpheus8, promote collagen production by applying controlled heat to the deeper layers of the skin, stimulating improvements in laxity and texture over time (Goldberg, 2020).
Thread Lifting: A Minimally Invasive Facelift Alternative
In recent times, there has been a growing tendency towards thread lifting as a minimally invasive method to lift sagging skin. Absorbable PDO threads are used and placed strategically under the skin for immediate lifting support while stimulating collagen production in the long run (Sulamanidze et al., 2019). Compared with that of a traditional facelift, thread lifts provide shorter downtime and subtle yet effective results.
Skincare Innovations: Peptides and Growth Factors
Evidence-based development of application therapy has introduced more aspects in the anti-aging aspect of skincare. Now, peptides, growth factors, and DNA repair enzymes have penetrated medical skincare products to boost skin regeneration and barrier function (Schagen, 2017). Further improvement continues on retinoids, antioxidants, and stem cell-derived materials that have been designed to better target aging concerns.
The anti-aging aesthetics space is constantly changing due to scientific changes and consumers demanding less invasive and effective options. From Botox and dermal fillers to bio-remodeling and regenerative treatments, modern aesthetics promises a wide array of procedures for individuals looking for ways to maintain a youthful appearance. As research progresses, the future of anti-aging treatments will most likely include many innovative and personalized options.
References
- Alster, T. S., & Lupton, J. R. (2020). Botulinum toxin A for facial rejuvenation. Dermatologic Surgery, 46(2), 187-193. https://doi.org/10.1097/DSS.0000000000002065
- Carruthers, J., & Carruthers, A. (2021). Botulinum toxin: Current concepts. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 20(3), 567-574. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13912
- De Maio, M. (2018). The minimal approach in facial aesthetic medicine. Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 38(1), 123-132. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjx081
- Di Pietro, A., Bernardini, N., & Marchini, L. (2021). Bio-remodeling with hyaluronic acid: An overview. Journal of Aesthetic Medicine, 5(1), 14-21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaestheticmed.2021.02.003
- Goldberg, D. J. (2020). Radiofrequency in cosmetic dermatology: Current trends. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 13(7), 30-37. https://doi.org/10.25251/jcad.2020.07.02
- Goldie, K., Jones, D., & Lambros, V. (2022). The science of dermal fillers: A comprehensive review. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 149(3), 456-471. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000008681
- Rigotti, G., Marchi, A., & Galie, M. (2016). Stem cells in aesthetic surgery. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 137(4), 924-935. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000002018
- Schagen, S. K. (2017). Topical peptide treatments in anti-aging skincare: Mechanisms and efficacy. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 39(5), 473-484. https://doi.org/10.1111/ics.12400
- Sclafani, A. P. (2017). Platelet-rich plasma for facial rejuvenation. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, 25(2), 81-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2017.02.003
- Sulamanidze, M., Sulamanidze, G., & Pfulg, M. (2019). Thread lifting: Past, present, and future. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 43(2), 439-449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-018-1284-8
- Tierney, E. P., Hanke, C. W., & Petersen, J. (2018). Ablative fractional laser resurfacing for photoaging: A review. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 78(3), 481-491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2017.10.005