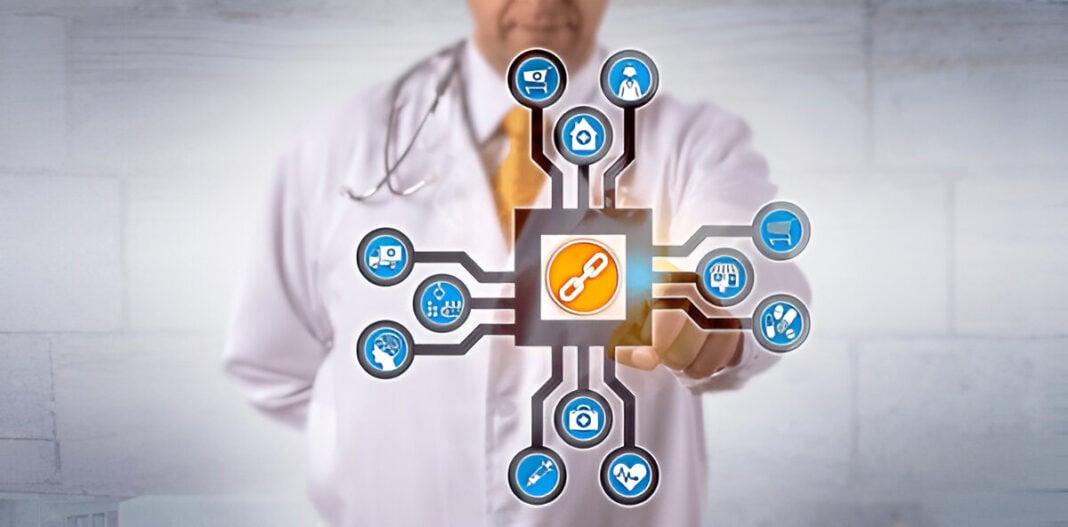
There is the management of patient records, a point of critical concern in dermatology. With documentation of medical history, diagnoses, and treatment that is accurate, safe and sound, patients live their lives, receiving effective and efficient care. Despite being widely used, traditional electronic health record (EHR) systems bring challenges in areas related to security, interoperability, and accessibility issues. Modern blockchain technology will serve as a paradigm shift because it creates a secure and decentralized but still tamper-proof system for managing dermatology records. Thus, the current article reviews the advantages, applications, challenges, and future possibilities regarding blockchain technology in dermatology from backed scientific research and industry contacts.
The Need for Blockchain in Dermatology Records
There is a huge volume of patient data with respect to dermatology, including but not limited to images, biopsies, prescriptions, and histories of treatment. Conventional patient EHRs tend to have security loopholes, inefficiencies in sharing data, and potential unauthorized accesses or breach of data (Zhang et al., 2018). Blockchain technology, which in fact ensures a distributed ledger system, is a solution to these problems of security, transparency, and patient control over medical data.
How Blockchain Works in Medical Record Management
The introduction of blockchain achieves transaction management in a decentralized manner across numerous nodes in a network. Each transaction, or “block,” is encrypted and chained to the previous one, thereby rendering an immutable chain of records (Kuo et al., 2017). Blockchain could assist in the secure storage and sharing of patient information in the context of dermatology while ensuring data integrity and privacy.
The key features of the blockchain in dermatology records are:
- Decentralization: No more centralized databases, which may become targets for cyberattacks or unauthorized modifications.
- Immutability: Recorded data cannot be altered or changed; this is a sure way of knowing that the medical history is preserved accurately.
- Smart Contracts: Self-implementing contracts that will enforce agreed data-sharing protocols amongst patients, healthcare providers, and the insurers.
- Patient Ownership: Medical records under the control of the patient with access given to the physician but also revoked at their discretion.
Benefits of Blockchain for Dermatology Records
1. Enhanced Security and Privacy
The hacking and data breach exposure of traditional medical databases are a prominent concern. Blockchain employs cryptographic procedures to protect the patient information so that only authorized personnel can gain access to sensitive pieces of information (Zhang et al., 2018).
2. Improved Interoperability
In fact, interoperability among various providers in dermatology is one of the burning concerns for the specialty. The blockchain allows easy transfer of data between dermatology, general practice, and other specialist providers to enhance coordination and efficiency in the management of treatment (Kuo et al., 2017).
3. Transparency and Trust
The integrity of blockchain creates a tamper-proof record of all transactions that guarantee transparency in medical record keeping. Such a feature may be used to verify clinical trials, insurance claims, and patient consent form processing.
4. Reduced Administrative Costs
Highly time-consuming paperwork still surrounds administrative duties in dermatology concerned with patient history verification and processing insurance claims. Blockchain automates these processes for low operating costs and increased efficiency (Nguyen et al., 2019).
5. Telemedicine and Remote Access
Due to the widespread practice of telemedicine and remote consultation of patients by dermatologists, the relevance of digital records for diagnosis and treatment has gained considerable attention in recent years. The mechanism of blockchain provides a secured system for the storage and sharing of medical images, allowing for proper and timely diagnosis without compromising the confidentiality of the patient.
Challenges and Considerations
Blockchain could have benefits in the field of dermatology, but these are not without challenges.
- Regulatory Compliance: Healthcare information is being governed by stricter rules as HIPAA, and GDPR. The implementation of necessary blockchain solutions should be well compliance within the legal framework.
- Scalability Issues: To an extent, the large-scale adoption of blockchain technology requires increased power for processing and storage capacity which becomes a technical problem (Nguyen et al., 2019).
- User Adoption: Healthcare provider and institution in training access to and use of blockchain applications to optimized benefits.
- Initial Costs: Development cost and initial investment on infrastructure create a barrier towards blockchain-based system adoption in many small clinics and dermatology practices.
Future Prospects
Advancements in technology eventually will solve the problems hindering the use of blockchain in dermatology in the near future. A few of them are as follows to improve the adoption of blockchain in medical records:
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI): Improving diagnosis and personalized treatment plans involves AI analysis of the dermatology data stored on BlockChain.
- Tokenization for Patient Incentives:Tokens in the blockchain can be incentivized to procure patient participation in clinical research and to induce sharing of anonymized data for research with scientific studies.
- Hybrid Models: A hybrid between blockchain and traditional EHR systems may be the best way to ensure security, compliance, and ease of use.
Blockchain technology has completely transformed the complex field of dermatology records by making it safe, transparent, and efficient. The decentralized and secure interoperability of patient data with other departments has made it possible for providers and patients to be cared for better without any unnecessary administrative hassles. There are still issues like regulatory compliance and scalability that need to be solved, but continuous improvement in blockchain technology is likely to spur increased usage even in dermatology and the whole healthcare sector at large.
References
- Kuo, T. T., Kim, H. E., & Ohno-Machado, L. (2017). Blockchain distributed ledger technologies for biomedical and health care applications. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 24(6), 1211-1220. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocx068
- Nguyen, D. C., Ding, M., Pathirana, P. N., & Seneviratne, A. (2019). Blockchain and AI-based solutions for patient data sharing and privacy preservation in healthcare. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 24(7), 2067-2079. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2019.2938609
- Zhang, P., Schmidt, D. C., White, J., & Lenz, G. (2018). Blockchain technology use cases in healthcare. Advances in Computers, 111, 1-41. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.adcom.2018.03.006