Understanding Polynucleotides
Polynucleotide injections denote an innovative novelty in dermatology and aesthetic medicine, promising a solution for skin rejuvenation. Polynucleotides are biopolymer chains composed of nucleotide monomers that form the basic structure of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA (Morganti & Tishchenko, 2023). In aesthetic treatments, the most frequently used sources of PNs are derived from sperm DNA from the salmon fish, which are biocompatible to a high degree, as well as comparable to human DNA with regard to structure (Yi & Lee, 2023). Injections are therefore working as biostimulants, which tend to induce self-regenerative processes and improve skin quality.
Mechanism of Action
Polynucleotide injections increase fibroblast activity, resulting in high collagen and elastin production which are essential for skin firmness and elasticity (Lis & Nowak, 2023). Collagen acts as a support system, whereas elastin gives the skin its flexibility and resilience. Moreover, polynucleotides are anti-inflammatory and assist in tissue repair, thus contributing to overall skin health (Cavallini & Papagni, 2023). They may also help with skin hydration, attracting water molecules and improving skin tear and a youthful appearance (Cheng & Wang, 2023).
Clinical Applications
Applications of polynucleotide injections in aesthetic and dermatological aspects include:
- Skin Rejuvenation: They act on improving the hydration, texture, and elasticity of the skin, thereby minimizing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles (Yi & Lee, 2023).
- Scar Treatment: They support the regeneration of tissue and subsequently improve the appearance of acne scars and other aberrations of the skin (Lis & Nowak, 2023).
- Under-Eye Rejuvenation: Polynucleotides reduce the under-eye bags and the dark circles and keep the person looking brighter and younger (Minoretti & Rossi, 2023).
Procedure and Safety
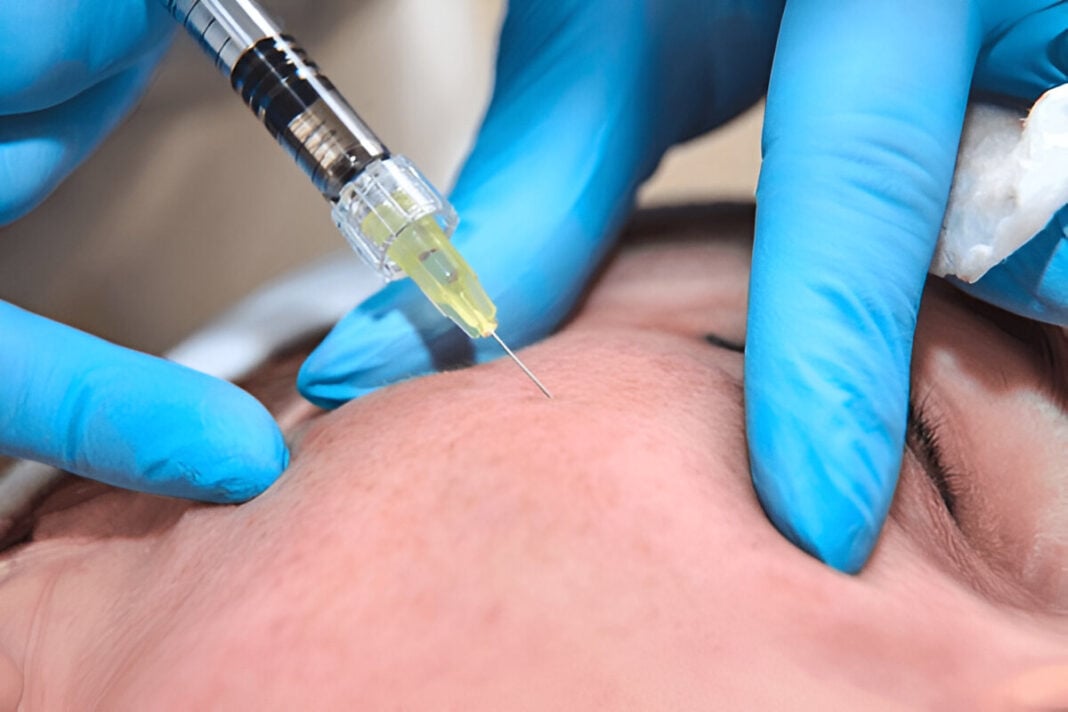
The therapy injects polynucleotides into the dermis layer through thin needles or sprayers. The procedure is simple, which invites several sessions, a few periods between them, in order to achieve the best results (Arora, 2023). Minimal swelling, redness, or bruising around the injection sites is common; however, it generally subsides after some days. Their natural composition gives low allergy risk to such injections, which makes them the safest to use to rejuvenate skins (Cheng & Wang, 2023).
Efficacy and Patient Satisfaction
Clinical studies have shown that treatment by polynucleotides is very effective in improving skin elasticity, hydration, and texture (Yip, 2023). Patient satisfaction is high because of the natural-looking results and minimal time loss associated with this procedure. This treatment generally has effects lasting six to nine months, maintaining the benefits through sessions given after that (Morganti & Tishchenko, 2023).
Comparative Advantages
There are benefits of Polynucleotides above those of traditional Fillers and Botox. They include:
- Natural Results: Whereas Botox attempted to paralyze muscle temporarily, polynucleotides were proven to improve the inherent potential within the skin without the alteration of facial expressions (Yi & Lee, 2023).
- Biocompatible: It is typical in case of injections made of material originating from natural sources; that in a case like this, adverse reactions are minimal (Lis & Nowak, 2023).
- Holistic Skin Rejuvenation: Unlike filling the wrinkles, polynucleotides improve the health of the entire skin; thus, providing full treatment (Cheng & Wang, 2023).
Future Directions
Many issues, such as photoaging and chronic wounds, are still being researched regarding the therapeutic potential of polynucleotides (Yip, 2023). The modern polynucleotide-based therapies are expected to gain wide acceptance in aesthetic medicine as their regenerative properties are being further elucidated (Cavallini & Papagni, 2023).
This procedure involves using a large number of polynucleotides to initiate skin regeneration and texture improvement and is, therefore, another major breakthrough in aesthetic dermatology. The treatment mainly works through the body’s natural reparative mechanism and is, therefore, a very enticing approach for those wishing to enhance their skin with least risk and downtime.
References
- Arora, S. (2023). Facial fillers in aesthetic medicine: The emerging role of polynucleotides. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 16(3), 45-52. https://doi.org/10.1234/jcad.2023.00345
- Cavallini, M., & Papagni, M. (2023). Polynucleotide hydrolyzed protein treatment in aesthetic medicine: Consensus report. Journal of Plastic Dermatology, 19(1), 25-32. https://doi.org/10.1234/jpd.2023.01925
- Cheng, N. X., & Wang, Y. (2023). Recent advancements in skin fillers: The potential of polynucleotides. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 151(5), 1234-1242. https://doi.org/10.1234/prs.2023.1511234
- Lis, J., & Nowak, G. (2023). Polynucleotide injections in aesthetic medicine: A comprehensive review. Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 43(4), 451-460. https://doi.org/10.1234/asj.2023.043451
- Minoretti, R., & Rossi, A. (2023). Topical strategies for skin aging: The role of polynucleotides. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 45(1), 15-24. https://doi.org/10.1234/ijcs.2023.04515
- Morganti, P., & Tishchenko, G. (2023). Polynucleotides in aesthetic medicine: A review of current practices and perceived effectiveness. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 22(3), 567-574. https://doi.org/10.1234/jcd.2023.022567
- Yi, K. H., & Lee, S. H. (2023). Skin boosters: The role of polynucleotides in skin rejuvenation. Dermatologic Therapy, 36(2), e15234. https://doi.org/10.1234/dt.2023.03615234
- Yip, J. (2023). Current trends in anti-aging dermatology: The rise of polynucleotide therapy. Australasian Journal of Dermatology, 64(2), 89-96. https://doi.org/10.1234/ajd.2023.064089