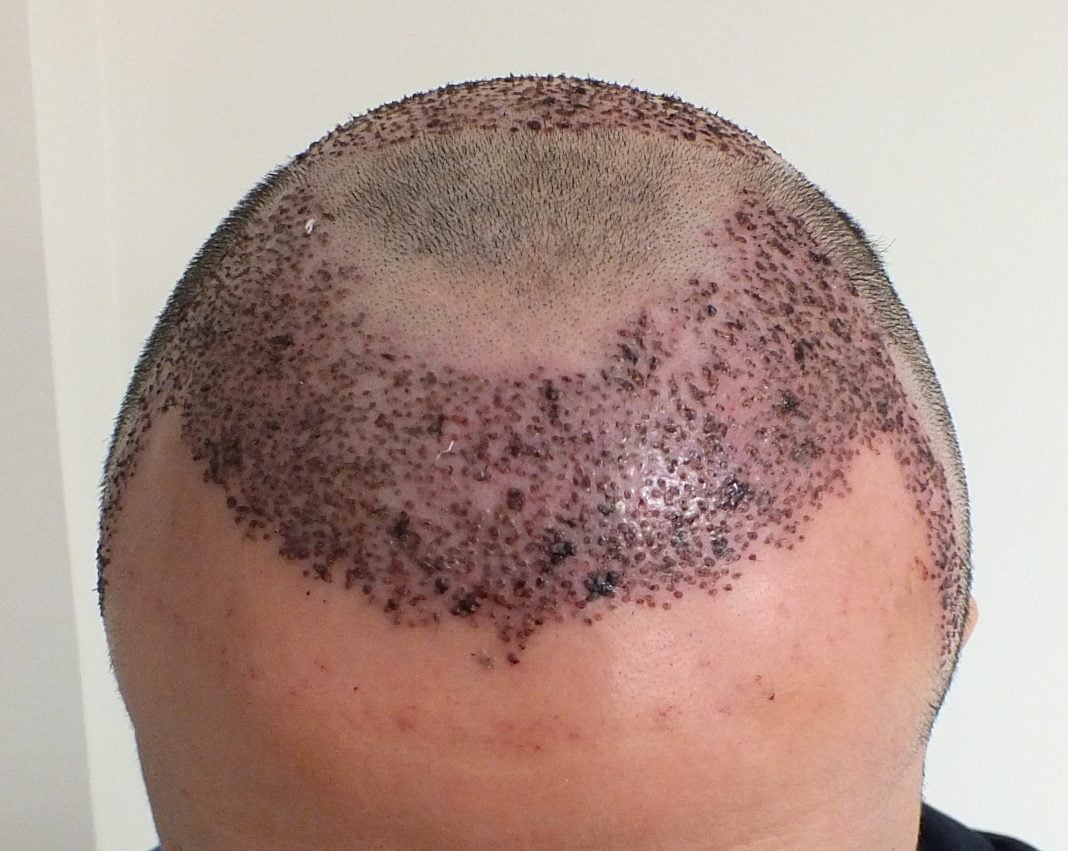
Millions of individuals across the globe are affected by hair loss or alopecia which creates a lot of psychological and social problems (Varothai & Bergfeld, 2014). Traditional treatments like medicines and hair transplants are often unsatisfactory for many people, and not all people can tolerate the treatments. Currently, there is a much newer and more advanced technology, biotechnology, providing options regarding lab-grown hair follicles. This new development lays a new pathway to combating baldness since tissues could be grown in controlled laboratory conditions, regrowing hair through the introduction of newly cultivated follicles.
The Science Behind Lab-Grown Hair Follicles
Do you know that hair follicles are tiny structures that have their own wall systems? They serve as the place where every hair grows. But due to dysfunction or loss of these tiny organs, there can be different types of hair loss. Researchers are actively doing experiments to find ways of bioengineering hair follicles with the use of stem cells, and tissue engineering techniques (Jahoda & Christiano, 2011). The aim is primarily to create functional hair follicles that can then be transplanted into the scalp for natural regrowth.
3D Printing and Stem Cell Research: In a groundbreaking study, scientists at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute successfully 3D-printed hair follicles within lab-grown human skin tissue (Science Daily, 2023). This achievement marked the first instance of generating hair follicles using 3D printing technology, highlighting the potential for in vitro follicle production for transplantation purposes. Similarly, researchers at the Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute developed a method to produce natural-looking hair using human-induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). These stem cells were differentiated into dermal papilla cells, which play a crucial role in hair follicle formation. When transplanted into the skin, these cells facilitated the growth of new hair through the epidermis, offering a potential therapeutic strategy for hair loss (Sanford Burnham Prebys, 2023).
Advancements and Clinical Applications
Ensuring the safety, efficacy, and scalability of hair follicles grown in the laboratory represent several challenges along the continuum of laboratory research to clinical application. Certain obstacles have been overcome by recent developments, which bring the technology much closer to clinical application.
Genetic Engineering and Hair Cell Development: In 2022, a group of asset startup biologists has used genetic engineering techniques into fresh hair-forming cells in an advancing condition toward a lab-grown hair follicles treatment option for baldness (Regalado, 2022). Further, a systematic review documented stem cell application in the treatment of male pattern baldness and other forms of alopecia; it emphasizes hair regeneration promising future treatments based on stem cell therapies that could be lab-grown hair follicles (Mysore et al., 2023).
Challenges and Future Directions
Though the advancement is very promising, the road ahead is still tricky before the laboratory-grown hair follicles can be used as a common remedy for baldness. Researchers are looking into factorscritical to the long-term survival and the proper integration of transplanted follicles, prevention of immune rejection, and orientation and density of hair naturally (Lee et al., 2020).
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations: Thorough testing to prove safety and efficacy has to be done with regard to animal studies as well as human clinical trials. Besides, getting regulatory approvals and ethical considerations will contribute a lot towards the mass adoption of this technology.
Conclusion
A significant milestone in the battle against baldness, the emergence of lab-grown hair follicles, opens new avenues for treatment. Using stem cells and tissue engineering, researchers are opening doors for possible therapies capable of enhancing hair growth and improving the quality of life for those suffering from hair loss. Continuing advances in research will only make perfect the horizon towards treating baldness with bioengineered hair follicles.
References
- Jahoda, C. A. B., & Christiano, A. M. (2011). Hair follicle regeneration: A perspective from the past, present, and future. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 131(12), 2174-2178. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.213
- Lee, W. J., Lee, S. H., Ahn, J., & Yoo, K. H. (2020). Recent advances in hair regeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(18), 6832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186832
- Mysore, V., Shashikumar, B. M., & Dhurat, R. (2023). Stem cell-based therapies for alopecia: Current perspectives. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 14, 112. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-023-03145-4
- Regalado, A. (2022, January 18). Baldness cure? Lab-grown hair cells move closer to reality. MIT Technology Review. https://www.technologyreview.com/2022/01/18/1043751/bald-lab-grown-hair-cells/
- Sanford Burnham Prebys. (2023). Functional hair follicles grown from stem cells. https://sbpdiscovery.org/press/functional-hair-follicles-grown-from-stem-cells
- Science Daily. (2023). 3D-printed hair follicles in lab-grown skin pave way for hair loss treatments. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2023/11/231115113440.htm
- Varothai, S., & Bergfeld, W. F. (2014). Androgenetic alopecia: An evidence-based treatment update. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology, 15(3), 217-230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-014-0077-5